Executive Summary
| Service Name: | Small Islands and Developing States (SIDS)* (TMCenter2015) |
| Country Name: | Timor Leste (tim) |
| Target Customers: | Citizens, Businesses, and other Agencies (possibly) |
Service Mission: Small Islands and Developing States (SIDS)* Overview
Small Islands and Developing States (SIDS)
Overview |
|
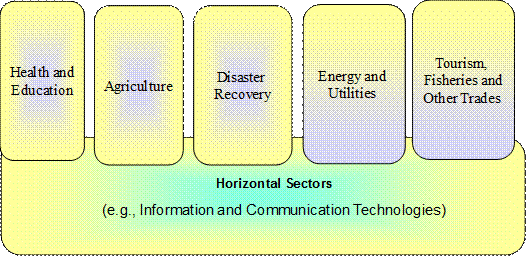
Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are small islands that are also least developed. SIDS face several challenges such as small populations, susceptibility to natural disasters, remoteness, and high communication, energy and transportation costs. The SIDS were first recognized as a distinct group of developing countries by the United Nations in 1992. The Barbados Programme of Action was produced in 1994 to assist the SIDS in their sustainable development efforts. The United Nations Office of the High Representative for the Least Developed Countries, Landlocked Developing Countries and Small Island Developing States (UN-OHRLLS) represents this group of states. Figure 1 is being used by the UN ICT4SIDS Partnership (www.ict4sids.com) to identify and address the unique challenges that are displayed as possible sectors by using the latest developments in ICTs. |
|
|
|
The following is a short summary of the main challenges.
1. Health and Education Due to the widely distributed populations in isolated communities, it is difficult to provided sustainable health and educational services to all the citizens of the islands. For example, Solomon Islands has a population of about 0.6 million people that are spread around 900 islands. Most remote communities are so small that education beyond 4th grade is not possible and availability of healthcare services is virtually non-existent.
2. Fisheries and Marine Resources For many SIDS the ocean and its vast resources are the firm basis upon which jobs and economic growth depend. The health of the oceans is not only vital to SIDS but to the global community at large. There is potential for private sector entities to partner with SIDS towards ensuring the sustainable management and utilization of ocean resources
Connectivity is crucial for SIDS to access the international marketplace, arrange the transport of goods, telecommunications or internet based transactions. Many SIDS continue to grapple with the high cost and infrequency of transport connectivity whether by sea or air. This is an area where partnerships between governments and private sector have great potential to yield improved transport links and achieve more efficient logistics.
Many SIDS are heavily dependent on fossil fuels for their energy needs. The efforts of the private sector can play a major role in developing affordable and competitive renewable energy sources that should lead to a significant shift from a high dependence on imported fossil fuels, to more sustainable locally harnessed energy sources.
5. Sustainable Agriculture Agriculture has historically been the foundation of cultural and economic activities in SIDS and today continues to play a significant role in sustaining livelihoods. There are opportunities for private sector entities to reinvigorate agricultural production in SIDS and contribute to the livelihoods of rural communities, for example, to help increase self-sufficiency in food production and take advantage of the international growth in organic agricultural produce.
SIDS' small and open economies leave them especially exposed and highly vulnerable to external shocks resulting from disasters. If resilience building is to be successful in the years to come, it will require active and concerted partnerships between various actors including governments, private sector and local communities. |
7. Sustainable Tourism
The travel and tourism industry is vitally important to SIDS. Private sector activities are a cornerstone of the viability of the tourism sector and reflect the importance of the sector in socio-economic development for SIDS. There is merit in further exploring how best tourism activities can be expanded, where capacity allows, and made more sustainable.
The UN ICT4SIDS Partnership is working with the UN-OHRLLS to address these and other unique challenges by using the latest developments in ICTs. Additional information is available at (www.ict4sids.com).
Selected Services
| Services | Status | Actions |
| Found | View it | |
| Not found | ||
| Not found | ||
| Found | View it | |
| Not found |
| Service Type: | Enterprise-Wide |
| Boundaries Crossed: | Federal |
| Use of Web: | No use of Web (Paper-based systems) |
| Use of Mobility: | No use of mobile computing |
Service Assessment Results
- Cost/Benifit Results: Should be Done Whenever Possible
- SWOT (Strengths, Weakness, Opportunities, Threats) Results: Worth Pursuing
- Acquisition Strategy Recommended:
Architecture View
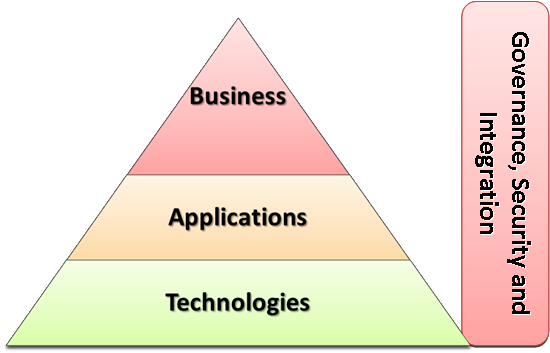
The strategic Planning Document provides information about different aspects of this architectural view. Additional documents generated by the system focus on different aspects of this view.
Following is the list of support documents generated by the system with brief description.
| Support Documents Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||