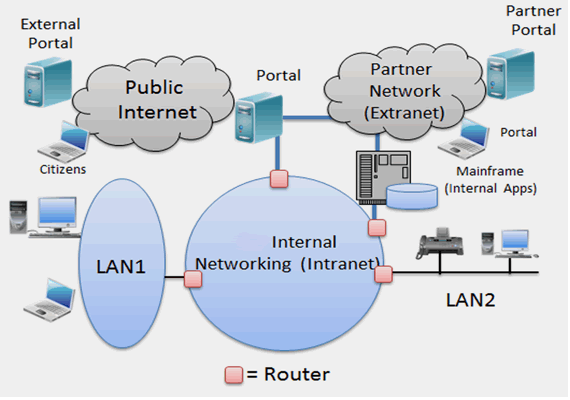
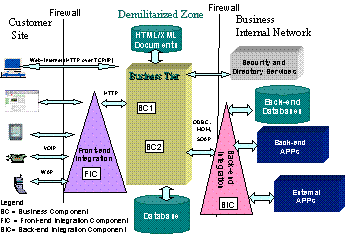
|
Sample Case Study: "How BI is used at Norfolk Southern to support decision making"?
Extracted from "Business Intelligence and Decision Support", by Turban, E et al, 9th edition, Prentice Hall.
Norfolk Southern, a scheduled railroad company, required new systems that would use statistical models to determine the best routes and connections to optimize railroad performance, and then apply the models to create the plan that would actually run the railroad operations. The new systems, called TOP (Thoroughbred Operating Plan) consists of the following key components:
-
An enterprise data warehouse (EDW) that makes data available to the TOP applications used in departments throughout the organization - including engineering, human resources (HR), and strategic planning.
-
A TOP dashboard application that pulls data from the enterprise data warehouse and then graphically depicts actual performance against the trip plan for both train performance and connection performance. The application uses visualization technology so that field managers can more easily interpret the large volumes of data (more than 160,000 weekly connections across the network).
-
An Access Network (AccessNS) that allows more than 1500 users from 8,000 customer organizations to log in and access predefined and custom reports about their accounts at any time. Users can access current data, which is updated hourly, or they can look at data from the past 3 years. AccessNS provides alerting and RSS feed capabilities
-
The HR applications use the data warehouse to determine where to locate its field offices in order to best meet the needs of Norfolk Southern's 30,000+ employees. These applications combine employee demographic data (e.g., zip codes) with geospatial data traditionally used by the Engineering Group. HR visually maps out the employee population density, making it easier to determine the best (optimal) locations for the field offices.
-
Norfolk uses the same enterprise data warehouse (EDW) for business intelligence and optimization of applications. The EDWmakes data available to all systems and applications that has allowed Norfolk Southern to offer self-service business intelligence. This innovative approach has setan example that other railroads have followed.
A Few Short Case Studies and Examples of BI and BIG DATA:
-
-
A Public Policy simulator ( www.outline.com) visualizes different aspects of a citizens relationship with the public sector. The public policy simulator helps people visualize the impact that public policies like health care reform and school budget changes might have on local economies and communities. It uses census information, IRS data and other public data to visualize how the public policy will impact different people before they are formally proposed.
-
IBM's Smarter Planet Initiative offers a wide array of BI and BIG DATA solutions for public safety, transportation, social services programs, tax and revenue and education. These products include predictive analytics and data mining tools. See the site www.ibm.com/smarterplanet/
-
Many police departments are using BI technologies to correlate traditional criminal justice information with data from traffic reports and transportation sources, building permits and social media activities to predict and prevent crimes before they happen.
-
SAS Fraud Framework helps agencies detect fraud, waste and abuse for government services such as Medicaid through its Visual Analytics solution.
Additional Sources for Case Studies and Examples:
Many examples of BI and BIG data are being published on a regular basis on the Internet. The following sources are highly recommended:
-
-
-
The well known textbook, by Efraim Turban et al on "Decision Support and Business Intelligence Systems" ( Prentice Hall, 10th edition, 2014) has almost 50 well written examples and case studies on BI and DSS. Every chapter, it has 14 chapters, has an opening vignette case study and then 4-5 more case studies/examples in each chapter.
-
The book by Cindi Howson, "Successful Business Intelligence: Unlock the Value of BI & Big Data" (McGraw- Hill, 2013) also has many practical examples of BIG DATA.
-
Many short examples of BIG DATA and BI in governments are published regularly in the in the www.govtech.com magazine.
|