|
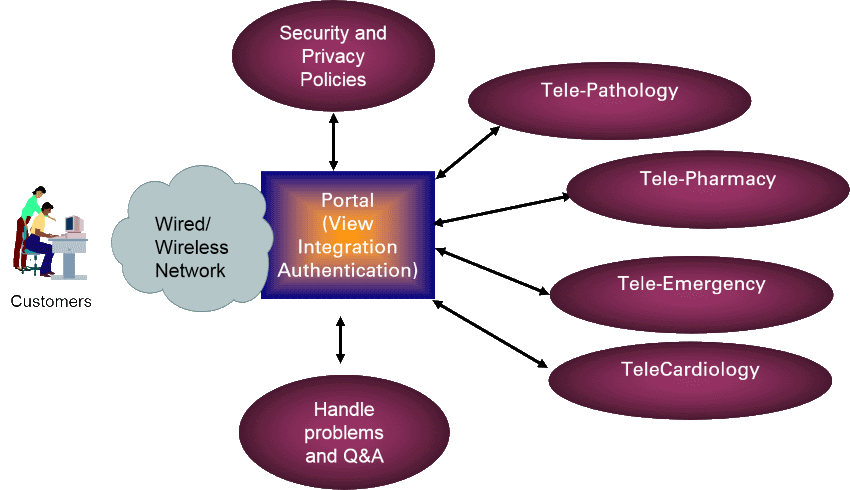
According to the American Telemedicine Association, telemedicine (sometimes called telehealth) is defined as "delivery of remote health services using technology". Specifically, Telemedicine is the use of telecommunication and information technologies in order to provide clinical health care at a distance. It helps eliminate distance barriers and can improve access to medical services that would often not be consistently available in distant rural communities. It is also used to save lives in critical care and emergency situations.
Telemedicine systems basically consist of the following approaches:
-
Store-and-forward: As the name suggests, uses technologies to collect medical information, store it in a central location and forward it to a provider or other destination. One of the most common forms of store-and-forward telemedicine is teleradiology, which allows radiologists to read nearly any study from workstations that are connected to the Internet. Teleradiology allows healthcare facilities to offer 24/7 services without having a radiologist on site.
-
Remote monitoring: This allows providers to receive health information from devices attached to, or utilized by, their patients. Providers can monitor the progress of their patients and the technology actually improves the patient’s outcome since the procedure could be performed while the patient was sleeping.
-
Interactive services: This involves providing care synchronously and/or asynchronously via telecommunication technologies. Interactive services may be as simple as a phone call between the provider and patient or as complex as telerobotic surgery. They may involve realtime information exchanges between the patient and the physician
|