|
Material requirements planning (MRP) is a production planning and inventory control system used to manage manufacturing processes. An MRP system allows each manufacturing unit to tell its supplier what parts it requires and when it requires them. An MRP system produces a detailed schedule of demands that identify the materials requirements, quantities, and target dates.
An MRP system is intended to simultaneously meet three objectives:
-
Ensure materials are available for production and products are available for delivery to customers.
-
Maintain the lowest possible material and product levels in store
-
Plan manufacturing activities, delivery schedules and purchasing activities.
The basic function of MRP system includes inventory control, bill of material processing and elementary scheduling. MRP helps organizations to maintain low inventory levels. It is used to plan manufacturing, purchasing and delivering activities.
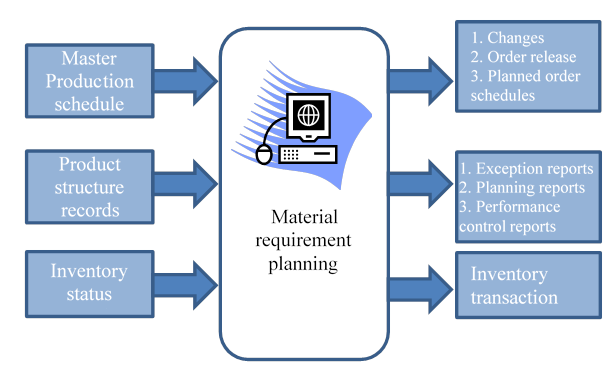
MRP is especially suited to PC manufacturing where the demand of many of the components and subassemblies depend on the demands of items that face external demands. Demands for end items are independent. In contrast, demand for components used to manufacture end items depend on the demands for the end items. The distinctions between independent and dependent demands are important in classifying inventory items and in developing systems to manage items within each demand classification. MRP systems were developed to cope better with dependent demand items. The three major inputs of an MRP system are the master production schedule, the product structure records, and the inventory status records. Without these basic inputs the MRP system cannot function.
The demand for end items is scheduled over a number of time periods and recorded on a master production schedule (MPS). The master production schedule expresses how much of each item is wanted and when it is wanted. The MPS is developed from forecasts and firm customer orders for end items, safety stock requirements, and internal orders. MRP takes the master schedule for end items and translates it into individual time-phased component requirements.
The product structure records, also known as bill of material records (BOM), contain information on every item or assembly required to produce end items. Information on each item, such as part number, description, quantity per assembly, next higher assembly, lead times, and quantity per end item, must be available.
The inventory status records contain the status of all items in inventory, including on hand inventory and scheduled receipts. These records must be kept up to date, with each receipt, disbursement, or withdrawal documented to maintain record integrity.
MRP will determine from the master production schedule and the product structure records the gross component requirements; the gross component requirements will be reduced by the available inventory as indicated in the inventory status records.
Figure 1 is a conceptual diagram of material requirement planning system.
|